Choosing the right lockable valve is crucial for safety and efficiency in various industries. According to a recent report by the Valve Manufacturers Association, the demand for lockable valves is projected to grow by 15% in 2026. With increasing regulations on safety and environmental protection, industries are emphasizing the need for reliable locking mechanisms.
John D. Wilson, a renowned expert in valve technology, stated, "Selecting the correct lockable valve can prevent catastrophic incidents and ensure compliance with industry standards." His insights reflect the critical nature of this decision. Choosing a lockable valve involves understanding operational requirements, pressures, and compatibility with fluids.
Nevertheless, many industries still overlook the importance of detailed specifications, leading to potential mishaps. The choice is not merely based on price, but functionality and reliability. A lockable valve must meet rigorous criteria to prevent unauthorized access. As we approach 2026, it’s essential to reevaluate choices and consider long-term safety impacts.

Lockable valves play a crucial role in various applications. Understanding the different types available is essential for effective use.
Manual lockable valves require human operation. They are simple but may pose risks if left unattended.
Automated valves offer convenience. They can be programmed, but this may lead to dependency on technology.
Another type is the quarter-turn lockable valve. This valve allows quick operation while providing security. It’s often used in water systems. Lastly, there are globe lockable valves. They offer precision but are not as quick to operate.
Choosing the right valve depends on specific needs. Consider the environment where it will be used. Do you need fast access, or is security a higher priority?
Assessing these factors can help navigate the options. A wrong choice could lead to leaks or failures.
Engaging with these decisions often requires more thought than expected.

Choosing the right lockable valve involves understanding your specific requirements. Assess the application where the valve will be used. Is it for water, gas, or chemicals? Each type demands unique features. Consider the operating environment, too. Is it indoors or outdoors? Will it face extreme temperatures or pressure? These factors impact your decision significantly.
Tip: Always check the material compatibility with your media. Corrosion resistance is crucial for longevity. Sometimes, a valve might look good on paper but fails in real-world conditions.
Also, think about the locking mechanism. Some valves offer simple manual locks, while others have more advanced options. Evaluate the ease of use. If a valve is hard to operate, it could lead to frustration in critical situations. Assessing your needs is not just about specs; it's about understanding how the valve will work for you daily.
Tip: Test different locking options if possible. Some locks may fail under stress. It’s vital to find what truly suits your situation. Remember, a poorly chosen valve can lead to leaks or failures, creating more issues down the line.
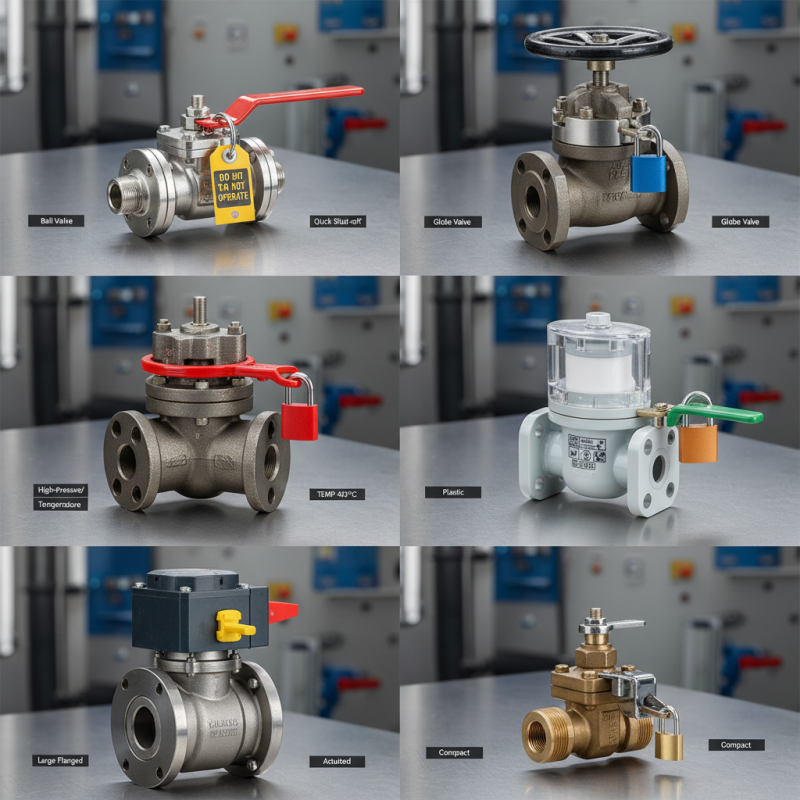

When selecting a lockable valve, several key features must be considered. Ensure the valve meets your specific application needs. The material of the valve plays a significant role in its durability and resistance to corrosion. According to industry reports, around 55% of valve failures occur due to improper material selection. Stainless steel is often preferred for its strength and longevity, but plastics can be suitable for certain environments.
Another critical feature is the locking mechanism. A reliable lock helps prevent unauthorized access. Some valves offer simple key locks, while others utilize more advanced electronic locking systems. Data shows that up to 30% of lockable valves fail because of inadequate locking mechanisms, leading to operational hazards. Look for designs that provide ease of use while ensuring safety.
Lastly, consider the size and compatibility of the valve. Incorrect sizing can lead to leaks and inefficient operation. A study indicated that 40% of maintenance issues stem from improperly sized valves. It is essential to closely match the valve's specifications with your existing piping systems. Even minor discrepancies may lead to costly repairs or replacements.
When choosing a lockable valve, material and durability are critical. A 2023 industry report reveals that over 70% of valve failures were due to material degradation. Common materials include stainless steel, brass, and PVC. Each offers different strengths. Stainless steel resists corrosion well, making it ideal for harsh environments. Brass, while durable, may corrode in seawater. PVC is lightweight but less durable under high pressure.
Evaluating these materials requires a keen eye for performance metrics. A durability test showed that stainless steel valves outlasted brass options by 40% in extreme conditions. However, improper installation can negate these advantages. Some users overlook maintenance. This can lead to unexpected failures, even in high-quality valves.
Choosing wisely means understanding your specific needs. Consider the working environment and the fluids involved. Not all lockable valves are created equal. A valve's durability is essential for reliable operation. Yet, user error can undermine even the best materials. Aim for a balance between quality and practicality to ensure longevity.
| Valve Type | Material | Durability Rating | Corrosion Resistance | Temperature Range (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ball Valve | Stainless Steel | High | Excellent | -20 to 120 |
| Gate Valve | Brass | Medium | Good | -10 to 80 |
| Butterfly Valve | PVC | Medium | Fair | 0 to 60 |
| Check Valve | Cast Iron | Low | Poor | -10 to 50 |
| Pressure Relief Valve | Aluminum | High | Very Good | -20 to 150 |
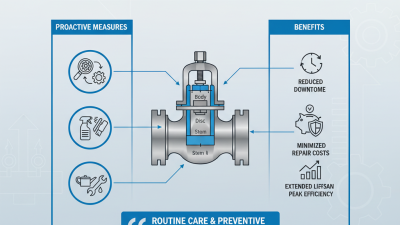
Installing a lockable valve requires careful consideration. Choose an appropriate location that allows easy access. Ensure it is not obstructed by other equipment. Mark the valve clearly for visibility. This helps in emergencies and routine checks.
During installation, use the manufacturer's guidelines. Improper installation can lead to leaks or malfunction. Tighten the fittings securely, but avoid over-tightening. This can damage the threads. Regular inspections are crucial. Look for corrosion or wear. If you spot issues, address them quickly.
Maintenance involves lubricating moving parts. This prevents rust and ensures smooth operation. Creating a maintenance schedule can be helpful. However, remember to check each valve’s specific needs. Not all valves require the same attention. Document any repairs or maintenance performed. Reflecting on your maintenance practices can improve future efforts.