Choosing the right Carbon Steel Valve Body is crucial for ensuring system reliability and performance. According to a recent market analysis by Valves International, the demand for carbon steel valve bodies has increased by over 20% in the past year. This growth is driven by industries such as oil and gas, where durability and corrosion resistance are paramount.
Industry expert John Smith, a noted valve technology specialist, emphasizes, "A well-chosen carbon steel valve body can significantly reduce maintenance costs." This highlights the importance of selecting the appropriate materials for specific applications. However, the decision-making process can often be flawed. Many overlook crucial factors like pressure ratings and temperature limits.
In practice, Carbon Steel Valve Bodies must be selected based on more than just cost. They should align with industry standards and application requirements. With a myriad of options available, some manufacturers still struggle to find the perfect fit. Therefore, understanding the key characteristics of carbon steel is essential to avoid costly mistakes.

When selecting carbon steel valve bodies, it's crucial to consider several factors. The operating environment plays a significant role. For instance, according to industry reports, 40% of failures in valves relate to corrosion issues. If the fluid transported is acidic or has particulates, you might face additional challenges. Different grades of carbon steel can provide varying levels of resistance against such factors.
Pressure and temperature ratings are also key. Most carbon steel valves are rated for medium to high pressures, but specific applications may require closer evaluation. Research indicates that about 30% of valve performance issues arise from mismatched pressure ratings. Understanding the exact conditions where the valve will operate helps avoid costly downtimes.
Additionally, the size and connection type should not be overlooked. A proper fit is essential for efficiency. Incompatible sizes can lead to leaks, increasing maintenance costs. As per industry data, nearly 25% of replacements could have been avoided by choosing the right size from the beginning. Balancing these considerations is vital for achieving reliability and long-term performance.
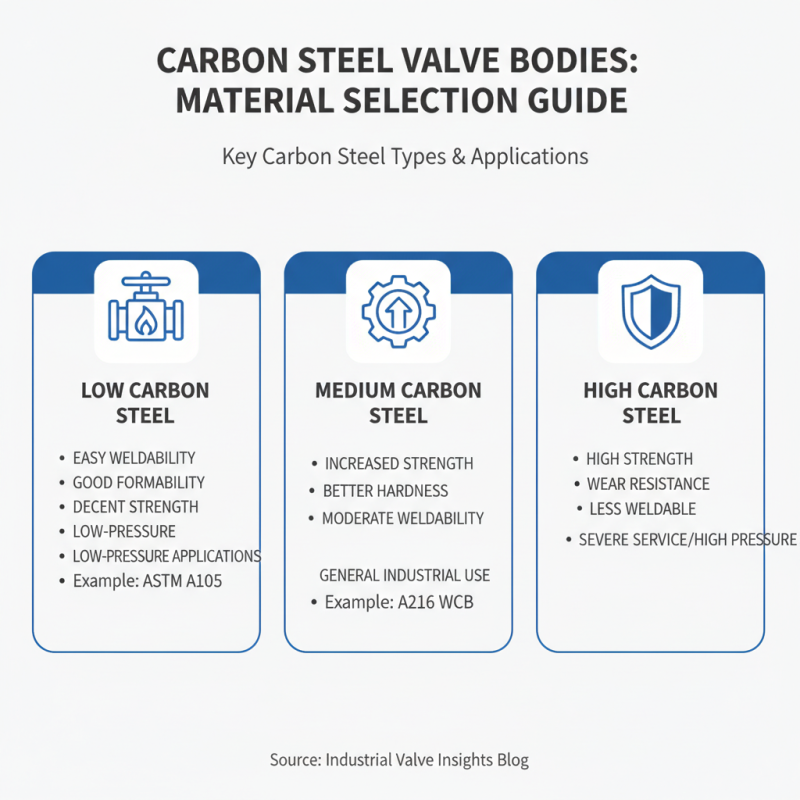
When choosing a carbon steel valve body, understanding the types of carbon steel materials is crucial. Various grades exist, each serving distinct applications. For instance, low carbon steel is popular for valves requiring good weldability. This material is easily formed and offers decent strength, making it suitable for low-pressure applications.
On the other hand, medium carbon steel provides enhanced strength and toughness. It is ideal for operational environments with higher stress. The increased carbon content allows for better hardness but may impact weldability. Careful consideration of this trade-off is necessary. High carbon steel, though very strong, might not be suitable for all valve designs due to its brittleness.
It’s essential to reflect on the environmental factors affecting your application. Corrosion resistance is a significant concern, and carbon steel may require additional coatings. Moreover, manufacturing methods can also impact material selection. Machining and molding processes may come with limitations. Balancing these factors leads to more informed decisions.
When considering carbon steel valve bodies, various industries come into play. These valves are widely used in oil and gas, water treatment, and manufacturing. Their durability is essential for handling high pressure and temperature variations. For instance, in the oil and gas sector, they manage the flow of crude or refined products. Water treatment plants use them to regulate the flow of treated water, ensuring safety and efficiency.
Tips: Always inspect the valve for signs of wear. Corrosion can weaken the structure over time, leading to failures. Understanding the environmental conditions of your application is crucial. High humidity can accelerate rusting.
Carbon steel valves also serve in construction. Here, they control water and gas lines. In manufacturing, they help maintain processes and safety standards. However, choosing the right type can be challenging. Not all valve bodies suit every application. Factors like pressure rating, temperature range, and media type play a role. It's important to ask the right questions before purchasing.
When comparing carbon steel valve bodies with other materials, it's essential to consider their unique properties. Carbon steel offers a great strength-to-weight ratio. It withstands high pressures and temperatures well, making it suitable for various applications. However, its susceptibility to corrosion can be a drawback in certain environments.
Stainless steel, for instance, resists rust and has a longer lifespan in harsh conditions. Yet, it may not handle extreme temperatures as effectively. Plastic valve bodies can be lightweight and resistant to chemicals, but they lack the strength for high-pressure systems. Each material has strengths and weaknesses.
Tip: Assess your application’s conditions. Are you working in a wet or corrosive environment? If so, you might want to avoid carbon steel.
Another area to reflect on is cost. Carbon steel valves are often more affordable than their stainless counterparts. However, the initial savings could turn into higher maintenance expenses over time, especially if corrosion becomes an issue.
Tip: Weigh long-term costs against initial prices. Sometimes, investing upfront can save money later.

Maintaining carbon steel valve bodies is crucial for optimal performance. These components face harsh environments and must be kept in top shape. Regular inspection can reveal early signs of wear and corrosion. According to industry reports, improper care leads to a 25% decrease in lifespan.
Tips: Clean the valve surfaces regularly to prevent rust. Use a suitable lubricant to enhance movement. Monitor for unusual noises or leaks that signal problems.
In practice, ensuring a proper seal is essential. Inadequate sealing can result in pressure loss and system inefficiency. Signs of failure might include leaks or difficulty in operation. An alarming 40% of system failures occur due to neglected valves. Regular maintenance can mitigate these issues significantly.